Business Analysts bridge the gap between various departments, technologies, and stakeholders to ensure businesses operate efficiently and achieve their goals. In this article we are going to discuss various types of Business Analyst classified acrossdomains, hierarchy, technology, and methodologies.
Types of Business Analyst
Domain-Based Classification
Business analysts often specialize in specific domains, allowing them to provide tailored insights for different industries:
Finance Business Analysts: These analysts delve into financial data, aiding in budgeting, forecasting, and investment decisions. Their insights contribute to sound financial strategies.
Healthcare Business Analysts: With a deep understanding of healthcare systems, they streamline processes, implement technology solutions, and ensure compliance with regulations.
Retail Business Analysts: These experts analyze consumer behavior, sales trends, and inventory management, optimizing pricing strategies, merchandising, and supply chain management.
Hierarchy-Based Classification
The hierarchy of business analysts reflects their experience and responsibilities within an organization:
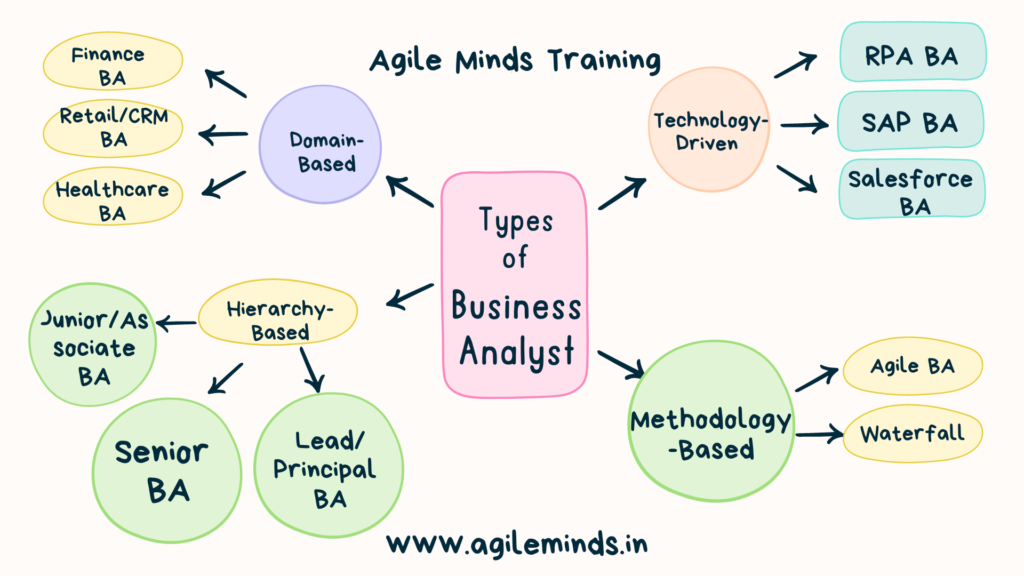
Junior/Associate Business Analysts: Entry-level analysts who assist with data collection, documentation, and basic analysis under the guidance of senior colleagues.
Senior Business Analysts: With extensive experience, these analysts lead projects, mentor junior staff, and provide vital insights to management.
Lead/Principal Business Analysts: Overseeing complex projects and managing analyst teams, they collaborate closely with top management to shape business strategies.
Technology-Driven Classification
Business analysts are embracing technology to streamline processes and drive innovation:
RPA Business Analysts: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) analysts focus on automating repetitive tasks using software bots, freeing up human resources for more strategic work.
SAP Business Analysts: SAP specialists bridge the gap between business processes and SAP technology, ensuring seamless integration and optimal utilization of SAP solutions.
Salesforce Business Analysts: These experts leverage Salesforce CRM technology to improve customer engagement, sales processes, and data-driven decision-making.
Methodology-Based Classification
Business analysts adopt different methodologies to suit project requirements:
Agile Business Analysts: Operating in Agile environments, these analysts prioritize flexibility and collaboration, working closely with cross-functional teams to iteratively deliver value.
Waterfall Business Analysts: In contrast, waterfall analysts follow a sequential approach, thoroughly defining requirements before moving on to development and testing phases.
Conclusion
The role of a business analyst is as diverse as the business landscape itself. Their ability to adapt, innovate, and translate complex data into actionable insights is invaluable to organizations striving for success. By understanding the classifications—based on functions, domains, hierarchy, technology, and methodologies—businesses can harness the skills of these professionals to drive growth, make informed decisions, and stay competitive in the ever-evolving marketplace. Whether it’s strategic planning, domain expertise, technological integration, or methodological adaptability, business analysts truly are the architects of business success. Enroll yourself to become a Business Analyst in our Bootcamp
Read this article on Medium.com
